Build a timeline-based video editor
This document describes on a high-level how the Remotion Player can be synchronized with a timeline.
Read this document for guidance on building a video editor with the following characteristics:
- Multiple tracks that overlay each other
- Items can be arbitrarily placed on a track
- Items can be of different types (e.g. video, audio, text, etc.)
Get the <Timeline> component
We offer a copy-pasteable <Timeline> component that follows Remotion's best practices and also already handles zoom.
If you want to save time and get a head start, you can purchase it in the Remotion Store.
You can also build your own timeline component.
The following steps will use the same approach we used to build our Timeline component.
Watch the "Build a video editor in React" talk
Watch the talk "Build a video editor in React" by Jonny Burger, the creator of Remotion here.
You'll receive an outline of how to build a timeline, canvas, captioning and exporting functionality in just 30 minutes.
Build your own timeline
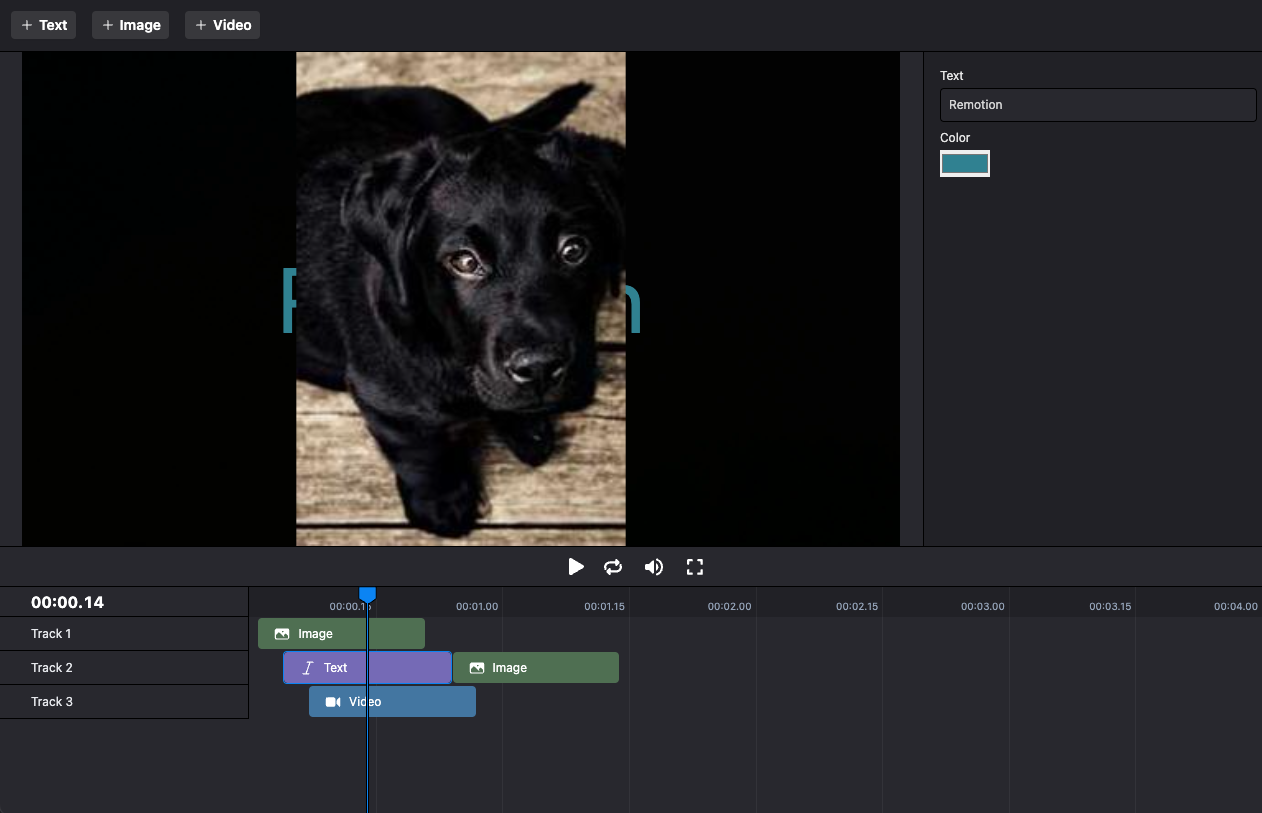
Define a TypeScript type
Item defining the different item types. Create another one for defining the shape of a Track:
types.tstsxBaseItem = {from : number;durationInFrames : number;id : string;};export typeSolidItem =BaseItem & {type : 'solid';color : string;};export typeTextItem =BaseItem & {type : 'text';text : string;color : string;};export typeVideoItem =BaseItem & {type : 'video';src : string;};export typeItem =SolidItem |TextItem |VideoItem ;export typeTrack = {name : string;items :Item [];};
remotion/Main.tsxtsxTrack ,Item } from './types';importReact from 'react';import {AbsoluteFill ,Sequence ,OffthreadVideo } from 'remotion';constItemComp :React .FC <{item :Item ;}> = ({item }) => {if (item .type === 'solid') {return <AbsoluteFill style ={{backgroundColor :item .color }} />;}if (item .type === 'text') {return <h1 >{item .text }</h1 >;}if (item .type === 'video') {return <OffthreadVideo src ={item .src } />;}throw newError (`Unknown item type: ${JSON .stringify (item )}`);};constTrack :React .FC <{track :Track ;}> = ({track }) => {return (<AbsoluteFill >{track .items .map ((item ) => {return (<Sequence key ={item .id }from ={item .from }durationInFrames ={item .durationInFrames }><ItemComp item ={item } /></Sequence >);})}</AbsoluteFill >);};export constMain :React .FC <{tracks :Track [];}> = ({tracks }) => {return (<AbsoluteFill >{tracks .map ((track ) => {return <Track track ={track }key ={track .name } />;})}</AbsoluteFill >);};
In CSS, the elements that are rendered at the bottom appear at the top. See: Layers
Render
a <Player /> component and pass the tracks as inputProps.
Editor.tsxtsxReact , {useMemo ,useState } from 'react';import {Player } from '@remotion/player';import type {Item } from './types';import {Main } from './remotion/Main';typeTrack = {name : string;items :Item [];};export constEditor = () => {const [tracks ,setTracks ] =useState <Track []>([{name : 'Track 1',items : []},{name : 'Track 2',items : []},]);constinputProps =useMemo (() => {return {tracks ,};}, [tracks ]);return (<><Player component ={Main }fps ={30}inputProps ={inputProps }durationInFrames ={600}compositionWidth ={1280}compositionHeight ={720} /></>);};
tracks state and can update it using the setTracks function.
We do not currently provide samples how to build a timeline component, since everybody has different needs and styling preferences.
An opinionated sample implementation is available for purchase in the Remotion Store.
remotion/Timeline.tsxtsxEditor :React .FC = () => {const [tracks ,setTracks ] =useState <Track []>([{name : 'Track 1',items : []},{name : 'Track 2',items : []},]);constinputProps =useMemo (() => {return {tracks ,};}, [tracks ]);return (<><Player component ={Main }fps ={30}inputProps ={inputProps }durationInFrames ={600}compositionWidth ={1280}compositionHeight ={720} /><Timeline tracks ={tracks }setTracks ={setTracks } /></>);};