Premountingv4.0.140
Remotion only ever renders the current frame.
This means when a video or another asset is about to come up, it is not loaded by default.
Even though the video is soon about to appear, it is not yet loaded because Remotion only ever renders the current time.
What is premounting?
Premounting is the practice of mounting a component containing assets earlier to allow assets some time to load before they appear.
The video is mounted earlier to give it some time to load.
It carries the style opacity: 0 to make it invisible.
It's time defined by useCurrentFrame() is frozen at 0.
Preloading a <Sequence>
From v5.0, all <Sequence> components are premounted for 1 second (fps frames) by default.
You can opt out by passing premountFor={0}.
In v4, add the premountFor prop to the <Sequence> component to enable premounting.
The number you pass is the number in frames you premount the component for.
Premounted.tsxconstMyComp :React .FC = () => { return ( <Sequence premountFor ={100}> <OffthreadVideo src ={staticFile ('bigbuckbunny.mp4')}></OffthreadVideo > </Sequence > ); };
In the Remotion Studio, a premounted component is indicated with diagonal stripes:
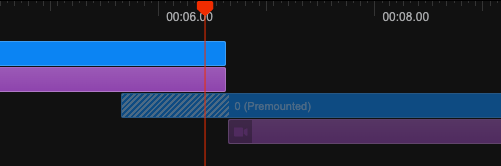
A premounted <Sequence> does carry the styles opacity: 0 and pointer-events: none.
It is not possible to premount a <Sequence> with layout="none" because such a sequence does not have a container to apply the styles to.
With <Series> and <TransitionSeries>
premountFor is also available on <Series.Sequence> and <TransitionSeries.Sequence>.
It is not yet possible to premount a whole <Series> or <TransitionSeries>.
Custom premount component
Premounting can also be implemented yourself with the public Remotion APIs.
Use the following component like you would <Sequence>:
PremountedSequence.tsximportReact , {forwardRef ,useMemo } from 'react'; import {Freeze ,Sequence ,SequenceProps ,useCurrentFrame ,useRemotionEnvironment } from 'remotion'; export typePremountedSequenceProps =SequenceProps & {premountFor : number; }; constPremountedSequenceRefForwardingFunction :React .ForwardRefRenderFunction <HTMLDivElement , {premountFor : number; } &SequenceProps > = ({premountFor , ...props },ref ) => { constframe =useCurrentFrame (); if (props .layout === 'none') { throw newError ('`<Premount>` does not support layout="none"'); } constenv =useRemotionEnvironment (); const {style :passedStyle ,from = 0, ...otherProps } =props ; constactive =frame <from &&frame >=from -premountFor && !env .isRendering ; conststyle :React .CSSProperties =useMemo (() => { return { ...passedStyle ,opacity :active ? 0 : 1, // @ts-ignore Only in the docs - it will not give a type error in a Remotion projectpointerEvents :active ? 'none' : (passedStyle ?.pointerEvents ?? 'auto'), }; }, [active ,passedStyle ]); return ( <Freeze frame ={from }active ={active }> <Sequence ref ={ref }name ={`<PremountedSequence premountFor={${premountFor }}>`}from ={from }style ={style } {...otherProps } /> </Freeze > ); }; export constPremountedSequence =forwardRef (PremountedSequenceRefForwardingFunction );
One caveat of this custom component: In a premounted sequence, the native buffer state can still be triggered.
It is your task to disable triggering the native buffer state (e.g set pauseWhenBuffering to false) when in a premounted sequence.
You can achieve this for example by using a React context.
Usage together with the buffer state
If you also use the buffer state, the <Html5Audio>, <Html5Video>, <OffthreadVideo> and <Img> tags are aware of premounting and don't trigger the buffer state while in a premounted <Sequence>.
Otherwise it would lead to pausing playback while a scene is not even visible yet.